Adhesives & Sealants Overview



Adhesives & Sealants Are All Around Us!
Every day we as a society reply upon adhesives and sealants for thousands of necessities, from our homes and offices to the vehicles we drive to the packaging that protects our food to the mobile devices we use. Adhesives and sealants are invisible, but they are everywhere.
There are countless ways adhesives and sealants make daily living not only possible but better!
The constantly increasing requirements being put on new consumer products is the driving force for technological progress: Nowadays, each new product that is developed must – as in the past – not only be better and more favorably priced than its predecessor, but must also meet the requirement of sustainability.
The consideration of environmental aspects means that the development of new products is becoming ever more demanding and that manufacturers must take into consideration more complex requirements for their new products. The increasing requirements put on products has since time immemorial been the key driving force for the development of advanced and new materials.
In addition to the classic metals, these materials include special alloys, plastics and also ceramics and glass. So-called composite materials, produced by combining different materials, have played a major role in this development.
Reinforced concrete is a well known composite material that has been around a long time. Newer composite materials are glass-fiber reinforced plastics and carbon fiber reinforced plastics which are used, for example, for constructing speed boats and yachts and increasingly also for car, rail vehicle and aircraft manufacture.
EXPLORE: Adhesive Technologies | Sealant Technologies
Did You Know?
Adhesives & sealants are used in…
Using adhesives over mechanical methods has advantages…
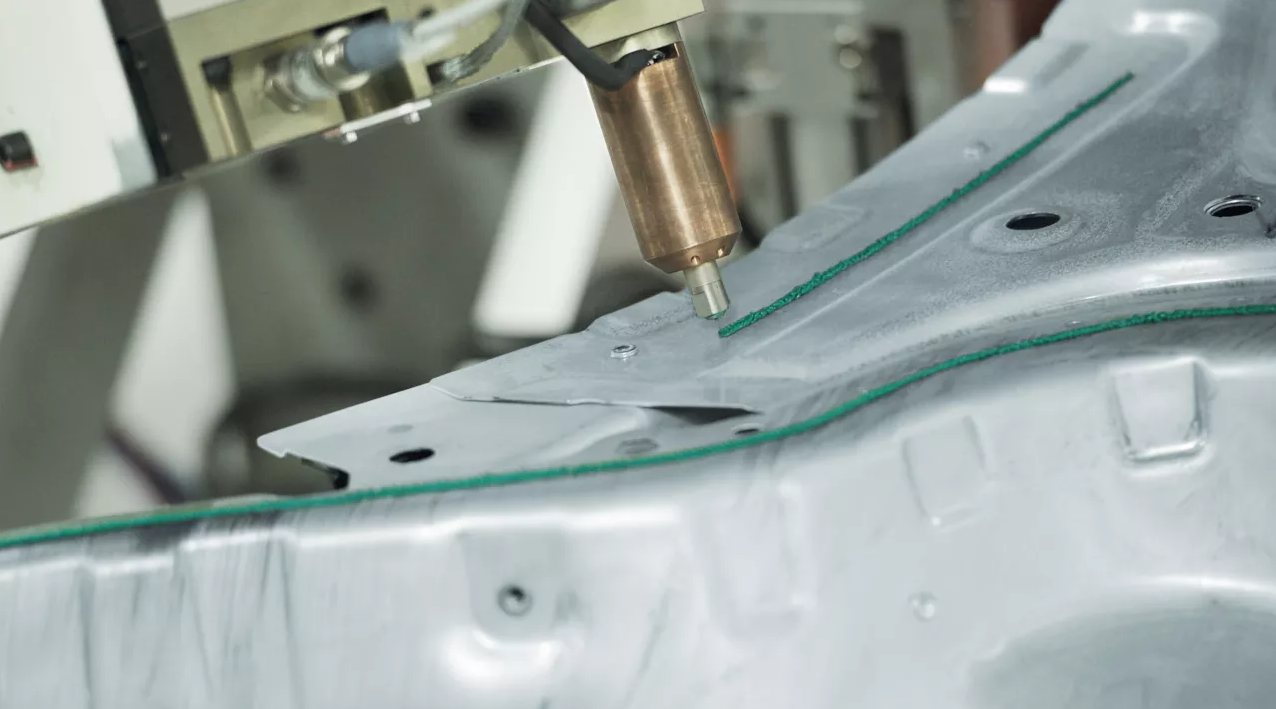
Transfer of high lap shear stresses due to the large bonding areas
Removal of unevenness on material surfaces; greater tolerances possible using gap-filling adhesives.
Prevention of contact corrosion for metal bonds, in contrast to when rivets or screws are used (the adhesive functions as an insulator.)

